Demystifying the D-MAP Structure: A Comprehensive Guide to Effective Data Management
Related Articles: Demystifying the D-MAP Structure: A Comprehensive Guide to Effective Data Management
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Demystifying the D-MAP Structure: A Comprehensive Guide to Effective Data Management. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Demystifying the D-MAP Structure: A Comprehensive Guide to Effective Data Management
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Demystifying the D-MAP Structure: A Comprehensive Guide to Effective Data Management
- 3.1 Understanding the D-MAP Structure: A Foundation for Data Organization
- 3.2 Unveiling the Benefits of the D-MAP Structure: A Catalyst for Data Efficiency
- 3.3 Real-World Applications of the D-MAP Structure: Transforming Data Management in Various Sectors
- 3.4 FAQs: Addressing Common Queries about the D-MAP Structure
- 3.5 Tips: Optimizing the D-MAP Structure for Maximum Impact
- 3.6 Conclusion: Empowering Data-Driven Decision-Making with the D-MAP Structure
- 4 Closure
Demystifying the D-MAP Structure: A Comprehensive Guide to Effective Data Management

In today’s data-driven world, efficient and organized data management is paramount. The D-MAP structure, a framework for organizing and structuring data, stands as a valuable tool for achieving this objective. This article delves into the intricacies of the D-MAP structure, elucidating its components, benefits, and practical applications.
Understanding the D-MAP Structure: A Foundation for Data Organization
D-MAP, an acronym for Data Management Architecture and Process, represents a structured approach to data management. It essentially provides a blueprint for organizing and managing data assets, ensuring consistency, accessibility, and integrity. The framework comprises four core elements:
1. Data Definition: This phase involves clearly defining the data elements, their attributes, and relationships. It encompasses identifying the data sources, understanding the data’s purpose, and establishing a comprehensive data dictionary.
2. Data Modeling: Here, the focus shifts to creating a visual representation of the data relationships. This involves designing data models, such as entity-relationship diagrams (ERDs), to depict how different data elements connect and interact.
3. Data Access and Integration: This crucial element focuses on establishing mechanisms for accessing and integrating data from various sources. It encompasses defining data access permissions, ensuring data consistency across different systems, and implementing data warehousing or data lakes for centralized storage.
4. Data Governance and Security: This final stage emphasizes establishing robust governance and security protocols. It involves defining data ownership, setting access controls, implementing data quality checks, and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations.
Unveiling the Benefits of the D-MAP Structure: A Catalyst for Data Efficiency
Implementing a D-MAP structure offers numerous benefits, including:
-
Improved Data Quality: By defining data elements and relationships clearly, D-MAP facilitates data validation and ensures data accuracy, reducing errors and inconsistencies.
-
Enhanced Data Accessibility: The framework promotes a centralized approach to data storage and access, making data readily available to authorized users for analysis and decision-making.
-
Increased Data Consistency: D-MAP ensures data consistency across different systems and platforms, eliminating data silos and fostering a unified view of information.
-
Streamlined Data Management: The structured approach simplifies data management processes, making it easier to track, update, and maintain data assets.
-
Enhanced Data Security: By implementing robust governance and security protocols, D-MAP protects sensitive data from unauthorized access and ensures compliance with data privacy regulations.
-
Improved Business Intelligence: With organized and accessible data, organizations can generate actionable insights and make informed decisions, leading to better business outcomes.
Real-World Applications of the D-MAP Structure: Transforming Data Management in Various Sectors
The D-MAP structure finds application across various industries and domains, enabling efficient data management and leveraging data for strategic advantage. Here are some examples:
-
Healthcare: Hospitals and healthcare providers can use D-MAP to manage patient data, ensuring data accuracy, privacy, and accessibility for clinical decision-making and research.
-
Finance: Financial institutions can leverage D-MAP to manage customer data, transaction records, and market data, enabling risk assessment, fraud detection, and personalized financial services.
-
E-commerce: Online retailers can employ D-MAP to manage product data, customer interactions, and sales transactions, optimizing inventory management, personalized recommendations, and marketing campaigns.
-
Manufacturing: Manufacturing companies can utilize D-MAP to manage production data, supply chain information, and quality control records, improving efficiency, optimizing processes, and enhancing product quality.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries about the D-MAP Structure
Q: What are the key challenges in implementing a D-MAP structure?
A: Implementing a D-MAP structure can present challenges, including:
-
Data Complexity: Managing large and diverse data sets can be complex, requiring skilled data professionals and robust tools.
-
Data Integration: Integrating data from multiple sources can be challenging due to data inconsistencies and varying formats.
-
Data Governance: Establishing and enforcing data governance policies can be complex, requiring clear roles and responsibilities.
-
Data Security: Ensuring data security in a constantly evolving threat landscape requires continuous vigilance and robust security measures.
Q: How can organizations ensure the success of their D-MAP implementation?
A: To ensure successful D-MAP implementation, organizations should:
-
Define clear objectives: Establish clear goals and objectives for the D-MAP implementation, outlining desired outcomes.
-
Obtain stakeholder buy-in: Engage stakeholders and secure their support for the initiative, ensuring alignment and commitment.
-
Choose the right tools and technologies: Select tools and technologies that align with the organization’s specific needs and data management requirements.
-
Implement a phased approach: Introduce the D-MAP structure in a phased manner, starting with pilot projects and gradually scaling up.
-
Continuously monitor and evaluate: Regularly monitor the effectiveness of the D-MAP structure, identify areas for improvement, and adapt the framework as needed.
Q: What are the key factors to consider when selecting a D-MAP solution?
A: When choosing a D-MAP solution, organizations should consider:
-
Scalability: Ensure the solution can accommodate the organization’s current and future data needs.
-
Flexibility: Select a solution that can adapt to evolving data management requirements.
-
Security: Prioritize a solution that offers robust security features to protect sensitive data.
-
Integration: Ensure the solution integrates seamlessly with existing systems and platforms.
-
Cost: Consider the cost of implementation, maintenance, and ongoing support.
Tips: Optimizing the D-MAP Structure for Maximum Impact
-
Start with a clear data inventory: Conduct a comprehensive inventory of existing data assets, identifying data sources, formats, and quality.
-
Define data ownership and responsibilities: Clearly define data ownership and responsibilities for data management, ensuring accountability and clear lines of authority.
-
Implement data quality checks: Establish data quality checks and validation processes to ensure data accuracy and integrity.
-
Embrace data governance: Develop and implement data governance policies and procedures to ensure data compliance, security, and ethical use.
-
Continuously monitor and improve: Regularly monitor the effectiveness of the D-MAP structure, identify areas for improvement, and adapt the framework as needed.
Conclusion: Empowering Data-Driven Decision-Making with the D-MAP Structure
The D-MAP structure provides a robust framework for organizing, managing, and leveraging data assets. By implementing a D-MAP structure, organizations can improve data quality, enhance accessibility, streamline management processes, and ensure data security. Ultimately, the D-MAP structure empowers organizations to make data-driven decisions, optimize business processes, and achieve their strategic objectives. As the data landscape continues to evolve, organizations must embrace structured data management approaches like D-MAP to navigate the complexities of data and unlock its full potential.
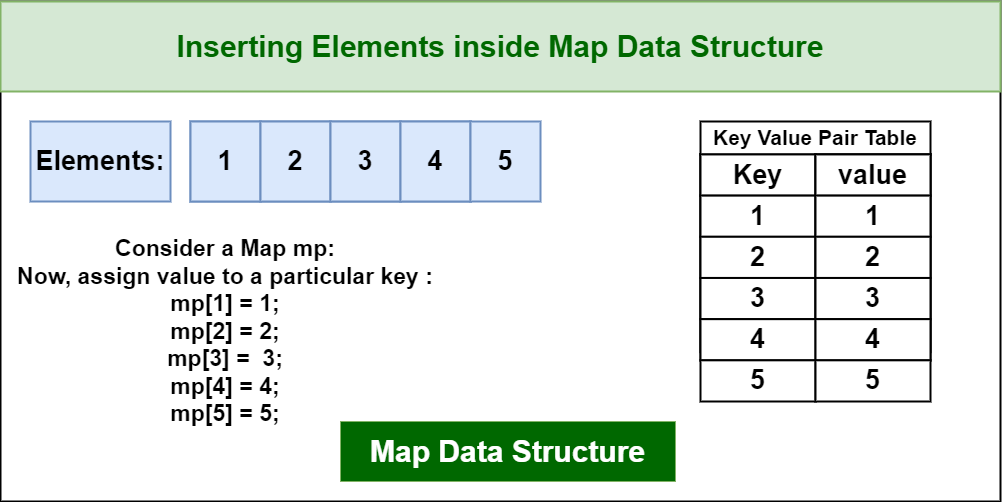

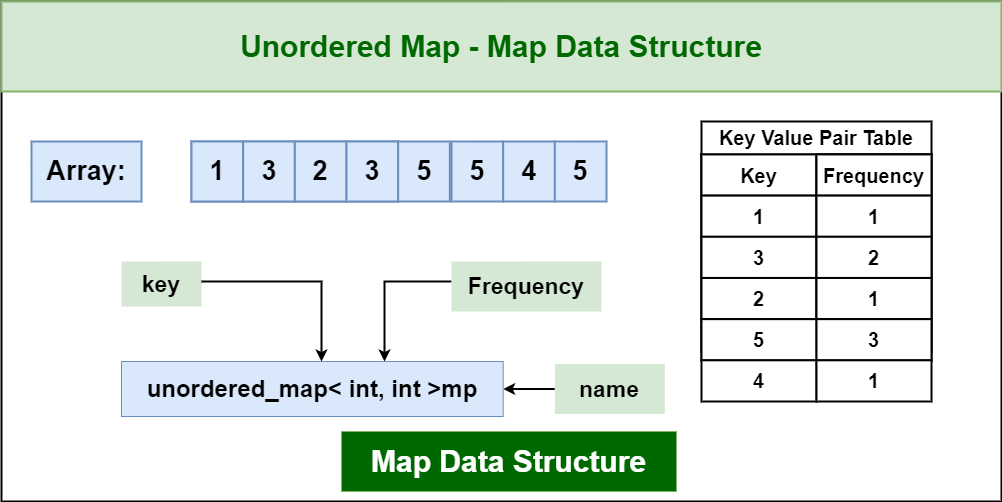


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Demystifying the D-MAP Structure: A Comprehensive Guide to Effective Data Management. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!