Demystifying the Significance of CAS Number: A Deep Dive into Dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP)
Related Articles: Demystifying the Significance of CAS Number: A Deep Dive into Dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP)
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Demystifying the Significance of CAS Number: A Deep Dive into Dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP). Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Demystifying the Significance of CAS Number: A Deep Dive into Dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP)

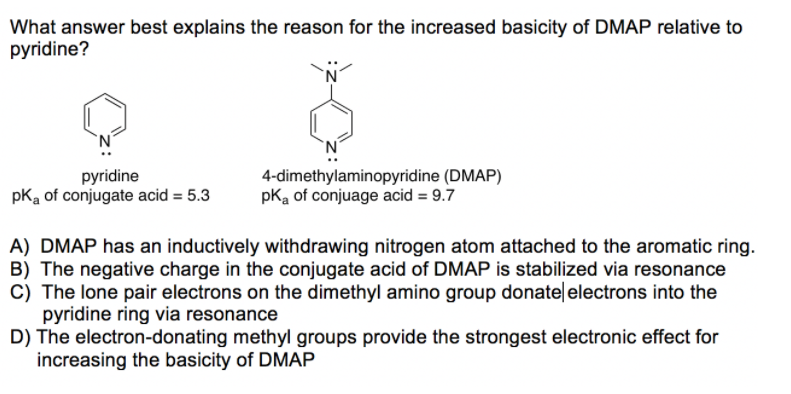
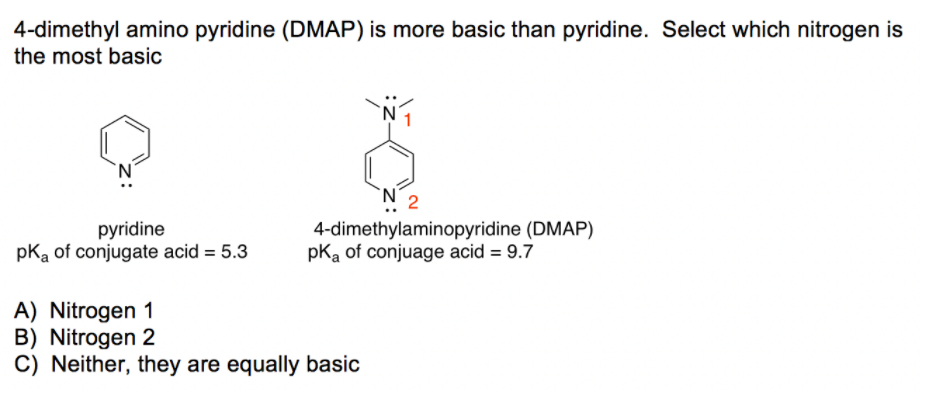
The realm of chemistry, particularly in the domain of organic synthesis, relies heavily on precise identification and characterization of chemical substances. One crucial tool employed for this purpose is the Chemical Abstracts Service (CAS) Registry Number, often referred to as a CAS number. This unique numerical identifier serves as a global standard for unambiguous identification of chemical compounds, including a widely used reagent known as dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP).
Understanding the Importance of CAS Numbers in Chemistry
The CAS Registry Number system plays a vital role in streamlining communication and ensuring accuracy within the scientific community. Here’s why:
- Uniqueness: Every chemical substance, regardless of its name or synonyms, is assigned a unique CAS number. This eliminates ambiguity and potential errors arising from variations in nomenclature.
- Global Recognition: The CAS Registry Number system is universally accepted and recognized, facilitating seamless communication and collaboration among researchers, manufacturers, and regulatory bodies worldwide.
- Data Access: CAS numbers serve as keys to accessing vast databases containing comprehensive information about chemical substances, including their properties, applications, safety data, and regulatory information.
Dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP): A Versatile Reagent with a Defined Identity
DMAP, with its CAS number [Insert CAS number of DMAP here], is a highly versatile reagent in organic chemistry. Its unique structure, featuring a pyridine ring with a dimethylamino group attached at the para position, grants it exceptional reactivity and catalytic properties.
Key Applications of DMAP in Organic Chemistry
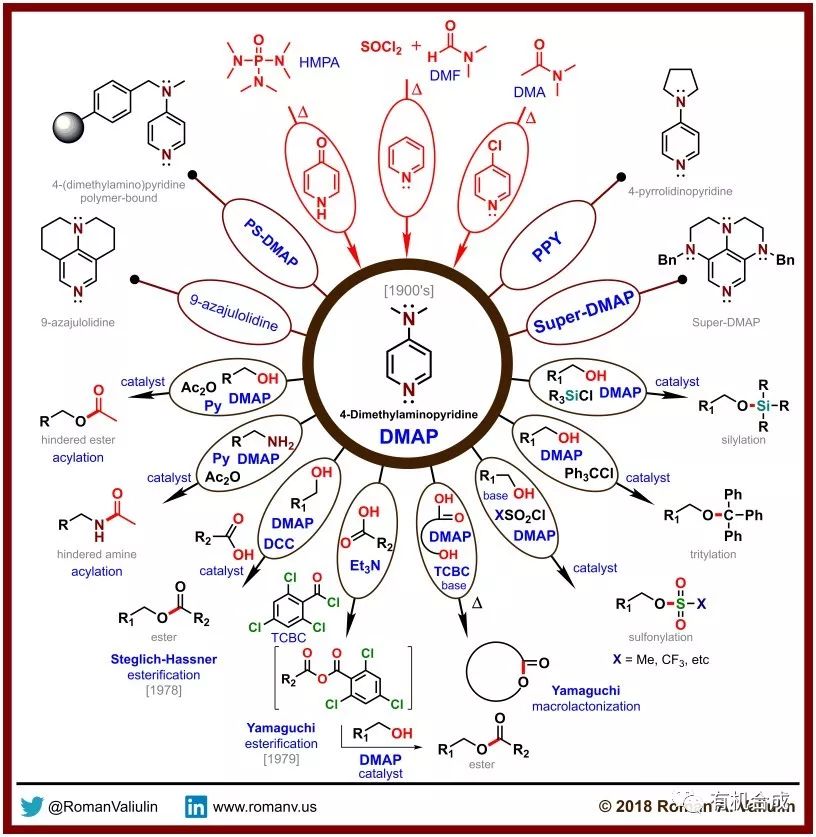
DMAP’s remarkable versatility makes it an indispensable tool in various organic synthesis applications, including:
- Acylation Reactions: DMAP acts as an efficient catalyst in the acylation of alcohols, amines, and phenols. Its ability to accelerate these reactions makes it highly valuable for the synthesis of esters, amides, and other carbonyl compounds.
- Esterification Reactions: DMAP’s catalytic activity is particularly prominent in esterification reactions, where it facilitates the formation of esters from carboxylic acids and alcohols.
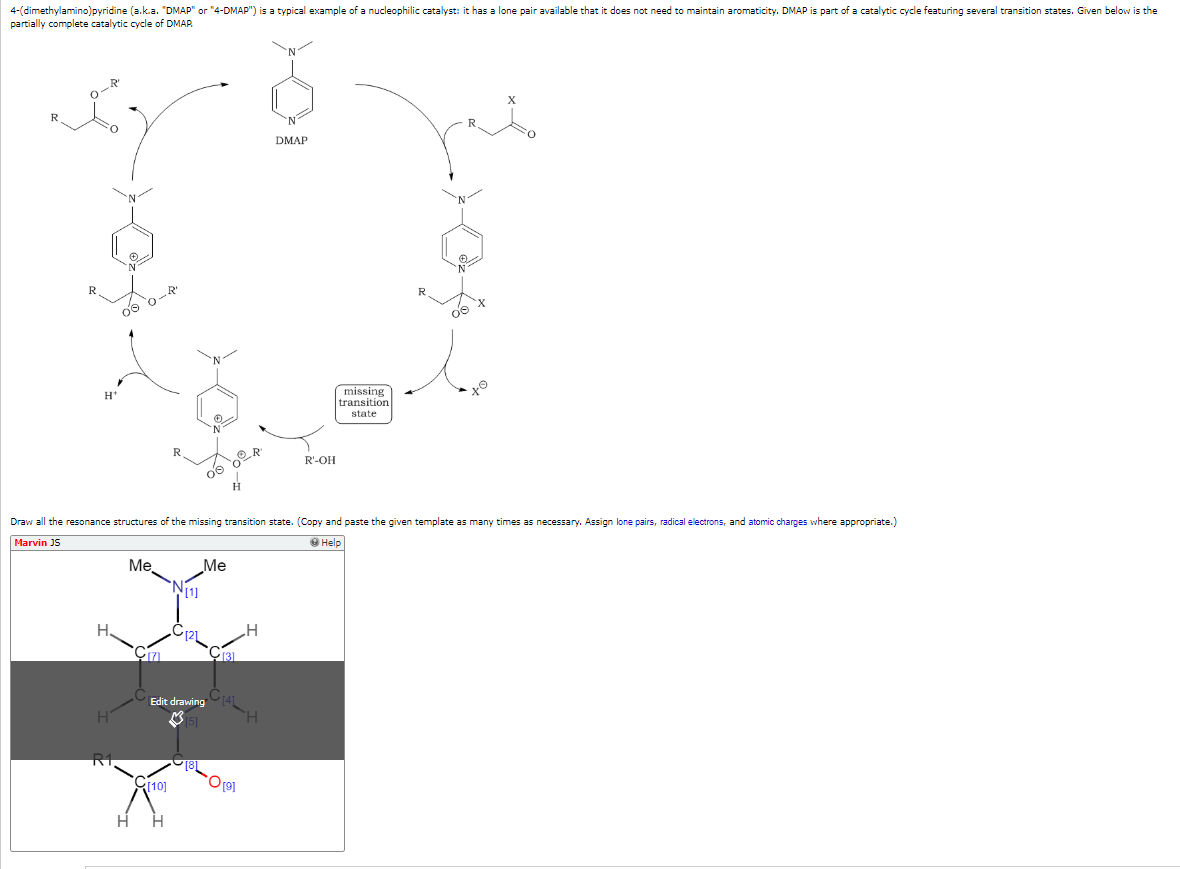
- Carbon-Carbon Bond Formation: DMAP plays a crucial role in promoting carbon-carbon bond formation reactions, such as the Michael addition and aldol condensation, contributing to the synthesis of complex organic molecules.
- Ring-Opening Reactions: DMAP’s catalytic properties extend to ring-opening reactions, particularly those involving lactones and lactams. Its ability to facilitate these reactions opens avenues for the synthesis of a wide range of cyclic and acyclic compounds.
Safety Considerations and Handling Procedures
While DMAP is a valuable reagent, it’s essential to handle it with appropriate safety precautions.
- Skin and Eye Contact: DMAP can cause irritation to the skin and eyes. It’s crucial to wear appropriate personal protective equipment, including gloves and eye protection, during handling.
- Inhalation: Inhaling DMAP vapors can lead to respiratory irritation. Adequate ventilation is essential when working with DMAP, and the use of a fume hood is strongly recommended.
- Storage: DMAP should be stored in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area, away from incompatible materials.
FAQs Regarding DMAP and its CAS Number
1. What is the significance of the CAS number for DMAP?
The CAS number for DMAP ([Insert CAS number of DMAP here]) serves as its unique identifier, ensuring unambiguous identification and facilitating communication and data access within the scientific community.
2. How can I find the CAS number for DMAP?
The CAS number for DMAP can be found in various databases and online resources, including the CAS Registry database itself, PubChem, and ChemSpider.
3. Why is DMAP a valuable reagent in organic chemistry?
DMAP’s versatility as a catalyst in acylation, esterification, carbon-carbon bond formation, and ring-opening reactions makes it a highly valuable reagent for organic synthesis.
4. What are the safety precautions associated with handling DMAP?
DMAP can cause skin and eye irritation and respiratory problems. It’s crucial to wear appropriate personal protective equipment, ensure adequate ventilation, and store it properly.
5. Where can I purchase DMAP?
DMAP is commercially available from various chemical suppliers. It’s essential to purchase from reputable suppliers to ensure the quality and purity of the reagent.
Tips for Using DMAP in Organic Synthesis
- Purity: Ensure the purity of DMAP before use, as impurities can affect reaction outcomes.
- Stoichiometry: Carefully determine the appropriate stoichiometry for the reaction to maximize yield and minimize side reactions.
- Solvent Selection: Choose an appropriate solvent for the reaction, considering DMAP’s solubility and the reaction conditions.
- Reaction Conditions: Optimize reaction conditions, such as temperature and time, for efficient conversion and desired product formation.
- Workup Procedures: Implement appropriate workup procedures to isolate and purify the desired product.
Conclusion: The Importance of DMAP and its CAS Number in Chemistry
The CAS number for DMAP ([Insert CAS number of DMAP here]) plays a crucial role in identifying this valuable reagent, ensuring accurate communication and data access within the scientific community. DMAP’s remarkable versatility as a catalyst in various organic reactions makes it an indispensable tool for chemists worldwide. Understanding the importance of CAS numbers and the properties of DMAP is essential for successful and safe chemical research and development.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Demystifying the Significance of CAS Number: A Deep Dive into Dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP). We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!