difference between concave mirror and convex
Related Articles: difference between concave mirror and convex
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to difference between concave mirror and convex. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Secrets of Curved Mirrors: Concave vs. Convex

Mirrors, those ubiquitous reflective surfaces, play a crucial role in our daily lives. From the simple act of brushing our teeth to the intricate workings of telescopes and medical imaging equipment, mirrors are indispensable tools. While most of us are familiar with the flat, planar mirrors found in our homes, the world of curved mirrors, specifically concave and convex mirrors, offers a fascinating glimpse into the realm of optics and its diverse applications.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Curved Mirrors
Before delving into the specifics of concave and convex mirrors, it’s essential to grasp the fundamental principles that govern their behavior. Both types of curved mirrors deviate from the flat surface of a plane mirror, creating a curvature that alters the reflection of light.
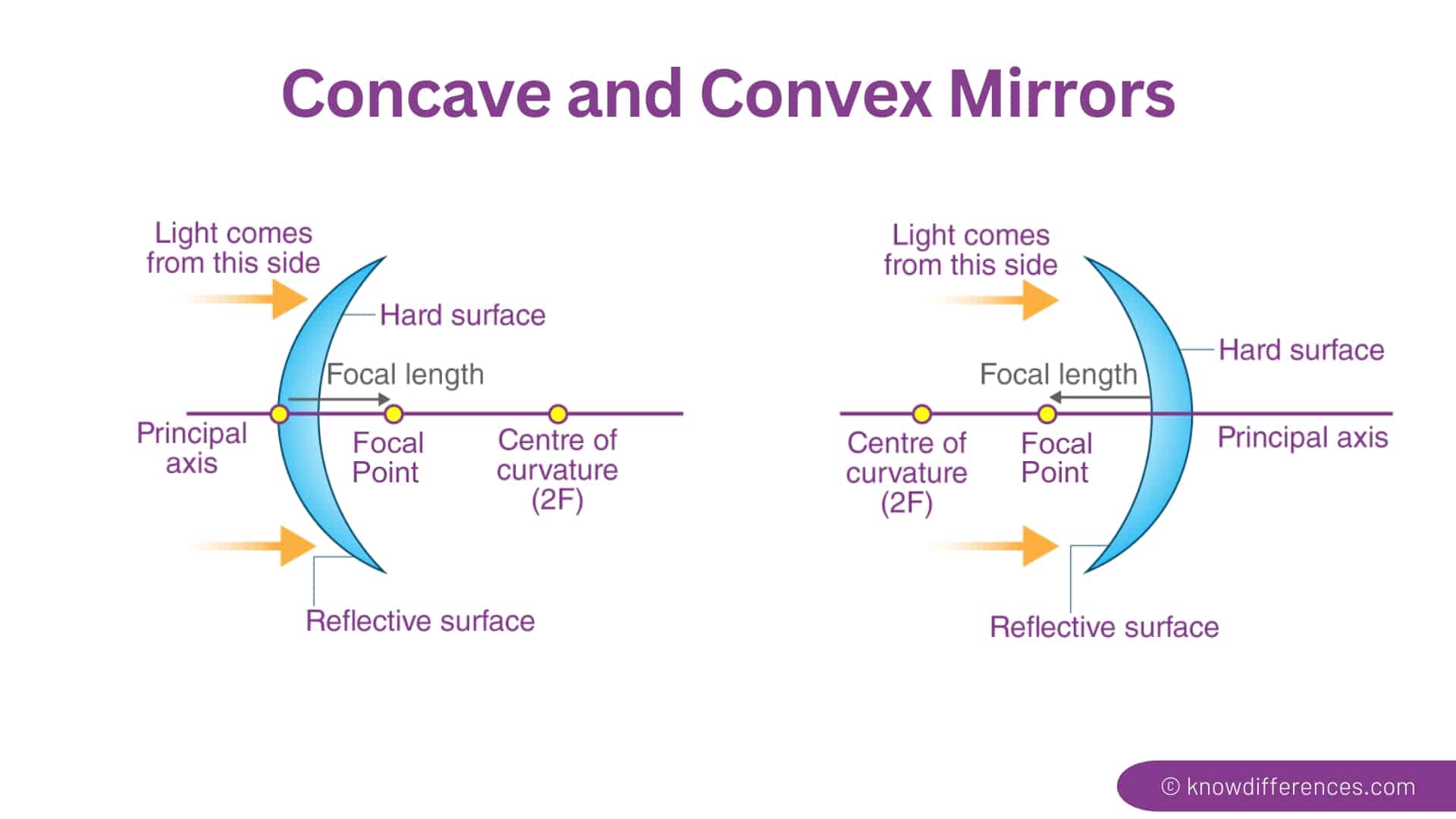
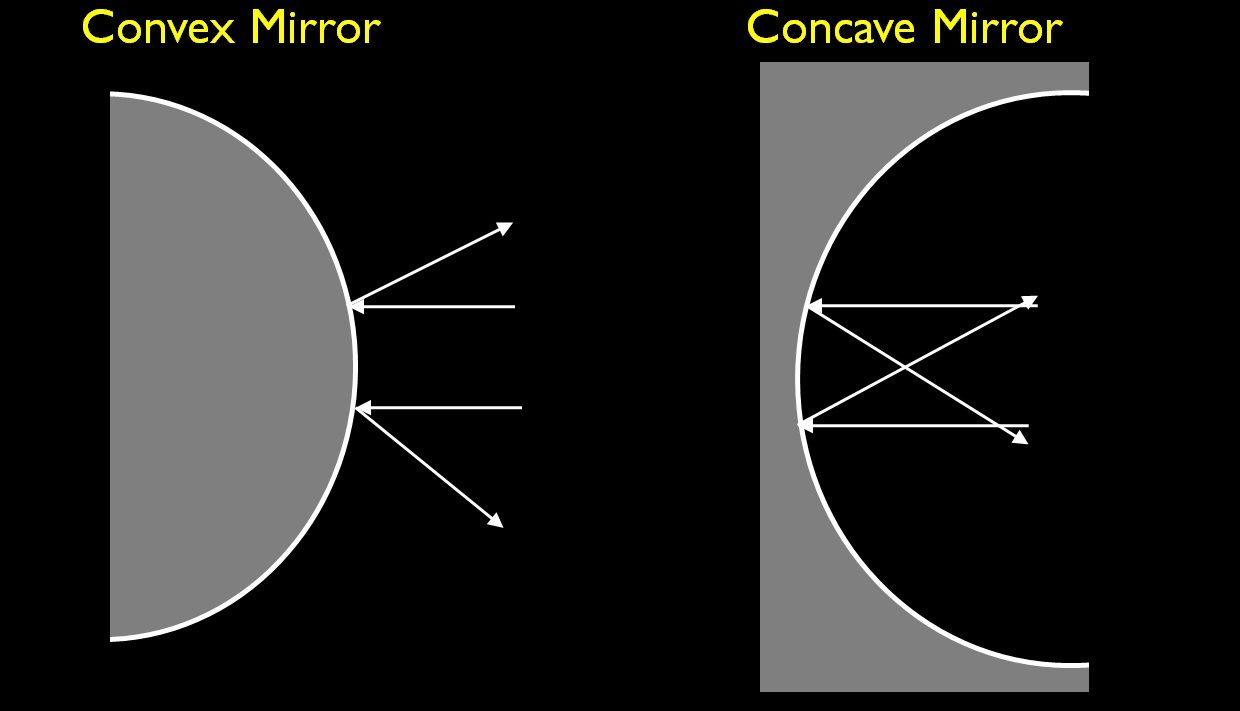
- Concave Mirrors: These mirrors have a reflecting surface that curves inwards, resembling the inside of a spoon. The inward curve creates a converging effect on light rays, bringing them together at a focal point.
- Convex Mirrors: In contrast, convex mirrors have a reflecting surface that curves outwards, similar to the back of a spoon. This outward curve causes light rays to diverge, spreading them out after reflection.
Exploring the Unique Characteristics of Concave Mirrors
Concave mirrors exhibit a fascinating array of optical properties, making them invaluable tools in various fields.
- Image Formation: Concave mirrors can form both real and virtual images depending on the object’s position relative to the mirror. When an object is placed beyond the focal point, a real, inverted image is formed. This image can be projected onto a screen. Conversely, when an object is placed between the focal point and the mirror, a virtual, upright, and magnified image is formed. This image cannot be projected onto a screen.
- Magnification: Concave mirrors are known for their ability to magnify objects. The degree of magnification depends on the object’s position relative to the mirror. Closer objects produce larger, more magnified images.
- Applications: The unique properties of concave mirrors make them indispensable in various applications. They are used in telescopes to gather and focus light from distant objects, in car headlights to create a concentrated beam of light, and in dental mirrors to provide magnified views of teeth.
Unveiling the Distinctive Traits of Convex Mirrors
Convex mirrors, with their outward curve, exhibit a distinct set of optical properties that set them apart from their concave counterparts.
- Image Formation: Convex mirrors always form virtual, upright, and diminished images, regardless of the object’s position. These images are smaller than the actual object and appear behind the mirror.
- Wide Field of View: Convex mirrors have a wider field of view compared to concave mirrors. This property stems from the diverging nature of light rays reflected from their surface.
- Applications: Convex mirrors are widely used in applications where a wide field of view is crucial. They serve as rear-view mirrors in vehicles, allowing drivers to see a broader area behind them. They also find applications in security systems, providing a wide view of a particular area.
Delving Deeper: The Role of the Focal Point
The focal point, a crucial concept in understanding curved mirrors, represents the point where parallel light rays converge after reflection from a concave mirror or where they appear to diverge from after reflection from a convex mirror. The distance between the mirror’s surface and the focal point is known as the focal length.
- Concave Mirror: In a concave mirror, the focal point lies in front of the mirror, and its focal length is positive.
- Convex Mirror: In a convex mirror, the focal point lies behind the mirror, and its focal length is negative.
The Importance of Understanding the Difference
The distinct properties of concave and convex mirrors stem from the curvature of their reflecting surfaces. This curvature dictates how light rays interact with the mirror, leading to the formation of different types of images and the ability to magnify or diminish objects. Understanding the difference between these two types of mirrors is crucial for various applications, from designing optical instruments to utilizing them in everyday life.
FAQs
Q1: How do concave and convex mirrors differ in their ability to form images?
A: Concave mirrors can form both real and virtual images, depending on the object’s position, while convex mirrors always form virtual, upright, and diminished images.
Q2: What is the significance of the focal point in curved mirrors?
A: The focal point determines the convergence or divergence of light rays reflected from the mirror and plays a crucial role in image formation.
Q3: What are some everyday applications of concave and convex mirrors?
A: Concave mirrors are used in telescopes, car headlights, and dental mirrors, while convex mirrors serve as rear-view mirrors in vehicles and in security systems.
Q4: How can I distinguish between a concave and a convex mirror?
A: A concave mirror curves inwards, while a convex mirror curves outwards. You can also identify them by their image formation properties: Concave mirrors can form both real and virtual images, while convex mirrors always form virtual images.
Tips for Understanding Concave and Convex Mirrors
- Visualize the curvature: Imagine a spoon. The inside of the spoon resembles a concave mirror, while the back resembles a convex mirror.
- Experiment with light: Shine a flashlight beam onto a concave and convex mirror. Observe how the light rays converge or diverge after reflection.
- Use diagrams: Draw ray diagrams to illustrate how light rays interact with concave and convex mirrors. This will help you visualize the image formation process.
- Research applications: Explore the diverse applications of concave and convex mirrors in different fields. This will provide a practical understanding of their importance.
Conclusion
Concave and convex mirrors, with their contrasting curvatures, offer a fascinating glimpse into the world of optics. Their unique properties, stemming from their ability to converge or diverge light rays, make them invaluable tools in various fields. Understanding the differences between these two types of mirrors is crucial for appreciating their diverse applications and for appreciating the elegance of optics. From telescopes to rear-view mirrors, concave and convex mirrors continue to play an essential role in our lives, shaping our understanding of the world around us.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into difference between concave mirror and convex. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!