Earth’s Atmosphere: A Protective Blanket for Life
Related Articles: Earth’s Atmosphere: A Protective Blanket for Life
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Earth’s Atmosphere: A Protective Blanket for Life. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Earth’s Atmosphere: A Protective Blanket for Life
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Earth’s Atmosphere: A Protective Blanket for Life
- 3.1 The Composition of Earth’s Atmosphere
- 3.2 Layers of the Atmosphere
- 3.3 Importance of Earth’s Atmosphere
- 3.4 Impacts on the Atmosphere
- 3.5 Protecting the Atmosphere
- 3.6 FAQs about Earth’s Atmosphere
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Earth’s Atmosphere: A Protective Blanket for Life

Earth’s atmosphere, the invisible layer of gases that surrounds our planet, is a vital component of life as we know it. It acts as a protective blanket, shielding us from harmful radiation, regulating temperature, and facilitating weather patterns. Understanding the composition and function of this delicate balance is crucial for appreciating its importance and safeguarding its integrity for future generations.
The Composition of Earth’s Atmosphere
Earth’s atmosphere is a complex mixture of gases, with nitrogen and oxygen dominating its composition.
Major Components:
- Nitrogen (N2): Comprises approximately 78% of the atmosphere. While inert, nitrogen is essential for plant growth and plays a crucial role in the nitrogen cycle.
- Oxygen (O2): Makes up about 21% of the atmosphere. It is vital for respiration, supporting the life of animals and plants.
- Argon (Ar): A noble gas, it accounts for almost 1% of the atmosphere and has minimal biological significance.
Minor Components:
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2): Though present in relatively small amounts (about 0.04%), carbon dioxide is a critical greenhouse gas, trapping heat and influencing global temperatures.
- Neon (Ne), Helium (He), Methane (CH4), Krypton (Kr), Hydrogen (H2), Ozone (O3): These gases are present in trace amounts, but each plays a specific role in atmospheric processes.
Variable Components:
- Water Vapor (H2O): The amount of water vapor in the atmosphere varies significantly depending on location and weather conditions. It is a crucial component of the water cycle and plays a major role in cloud formation and precipitation.
- Aerosols: These are tiny particles suspended in the atmosphere, including dust, smoke, sea salt, and volcanic ash. They can influence cloud formation, scatter sunlight, and affect air quality.
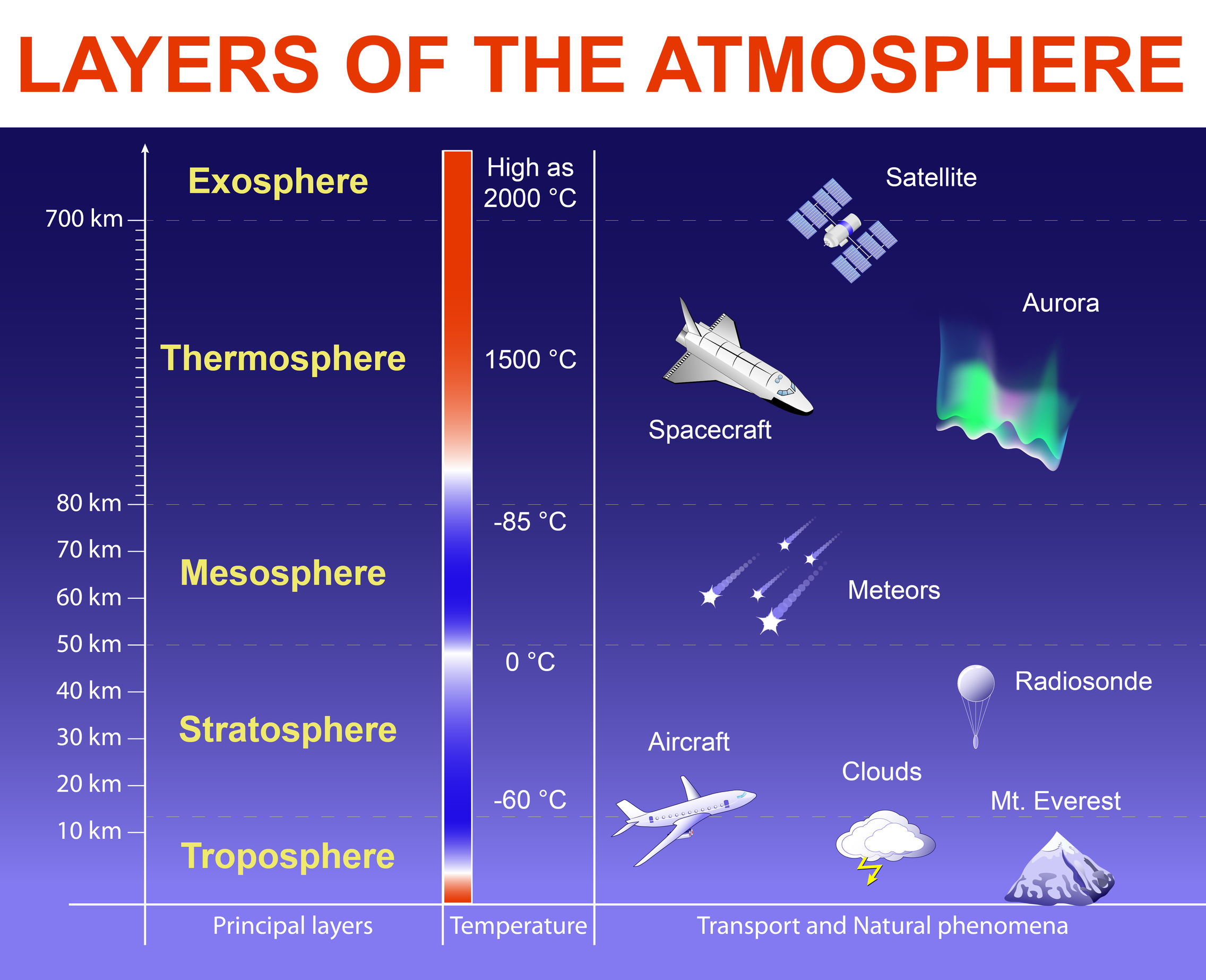
Layers of the Atmosphere
The Earth’s atmosphere is not a uniform layer but is divided into distinct layers based on temperature variations.
- Troposphere: This is the lowest layer, extending from the Earth’s surface to about 10-15 kilometers. It contains most of the atmosphere’s mass and is where weather occurs. Temperature generally decreases with altitude in this layer.
- Stratosphere: Extending from the top of the troposphere to about 50 kilometers, the stratosphere is characterized by a temperature inversion, where temperature increases with altitude. This layer contains the ozone layer, which absorbs harmful ultraviolet radiation from the sun.
- Mesosphere: This layer extends from the top of the stratosphere to about 85 kilometers. Temperature decreases with altitude in the mesosphere, reaching its coldest point at the mesopause.
- Thermosphere: Extending from the mesosphere to about 600 kilometers, the thermosphere experiences a significant temperature increase due to the absorption of solar radiation.
- Exosphere: This outermost layer gradually merges with outer space and is characterized by extremely low densities of gases.
Importance of Earth’s Atmosphere
Earth’s atmosphere is essential for life, providing numerous vital functions:
1. Protection from Harmful Radiation: The ozone layer in the stratosphere absorbs most of the sun’s harmful ultraviolet radiation, protecting life on Earth from damaging effects.
2. Temperature Regulation: The atmosphere acts as a blanket, trapping heat from the sun and preventing extreme temperature variations between day and night. Greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, play a crucial role in this process.
3. Weather and Climate: The atmosphere drives weather patterns, distributing heat and moisture around the globe. Atmospheric circulation patterns, such as jet streams, influence climate and weather events.
4. Respiration: Oxygen in the atmosphere is essential for respiration, allowing animals and plants to breathe and survive.
5. Sound Transmission: The atmosphere allows sound waves to travel, enabling communication and the perception of our surroundings.
6. Combustion: The atmosphere provides the oxygen necessary for combustion, allowing us to harness fire for various purposes.
7. Protection from Meteoroids: The atmosphere acts as a shield against small meteoroids, burning them up before they reach the Earth’s surface.
Impacts on the Atmosphere
Human activities have significant impacts on the Earth’s atmosphere, leading to various environmental challenges:
1. Air Pollution: Industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, and other sources release pollutants into the atmosphere, affecting air quality and human health.
2. Climate Change: The increasing concentration of greenhouse gases, primarily due to the burning of fossil fuels, is causing global warming and altering climate patterns.
3. Ozone Depletion: The release of certain chemicals, such as chlorofluorocarbons, has led to depletion of the ozone layer, increasing the amount of harmful UV radiation reaching the Earth’s surface.
4. Acid Rain: The release of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides from industrial activities can form sulfuric and nitric acid in the atmosphere, leading to acid rain, which damages ecosystems and infrastructure.
Protecting the Atmosphere
Preserving the health of Earth’s atmosphere is crucial for sustaining life on our planet.
1. Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Shifting to renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and promoting sustainable practices can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate climate change.
2. Combat Air Pollution: Implementing stricter regulations on industrial emissions, promoting cleaner transportation options, and encouraging the use of renewable energy sources can improve air quality.
3. Protect the Ozone Layer: Phasing out ozone-depleting substances, such as chlorofluorocarbons, has been successful in mitigating ozone depletion.
4. Sustainable Practices: Adopting sustainable practices, such as reducing consumption, recycling, and conserving resources, can minimize the impact of human activities on the atmosphere.
5. Environmental Awareness: Raising awareness about the importance of the atmosphere and the consequences of its degradation is crucial for promoting responsible behavior and fostering environmental stewardship.
FAQs about Earth’s Atmosphere
1. What is the difference between weather and climate?
Weather refers to the short-term atmospheric conditions at a specific location, such as temperature, precipitation, wind speed, and cloud cover. Climate, on the other hand, describes the long-term average weather patterns in a region.
2. How does the atmosphere protect us from meteoroids?
As meteoroids enter the Earth’s atmosphere, they experience friction with the air molecules, causing them to heat up and burn. This process, known as ablation, often vaporizes smaller meteoroids before they reach the ground.
3. What is the greenhouse effect?
The greenhouse effect is a natural process where certain gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, trap heat from the sun, warming the Earth’s surface. This effect is essential for maintaining a habitable temperature on Earth. However, excessive greenhouse gas emissions due to human activities are enhancing this effect, leading to global warming.
4. How does the atmosphere influence weather patterns?
The atmosphere’s temperature variations, pressure gradients, and moisture content drive weather patterns. Differences in temperature create pressure differences, which drive winds. Moisture in the atmosphere leads to cloud formation and precipitation.
5. What are the consequences of air pollution?
Air pollution can lead to various health problems, including respiratory illnesses, cardiovascular diseases, and cancer. It can also damage ecosystems, reduce visibility, and contribute to acid rain.
6. How can we reduce our carbon footprint?
Reducing our carbon footprint involves minimizing our greenhouse gas emissions. This can be achieved by using energy-efficient appliances, switching to renewable energy sources, reducing our reliance on private vehicles, and adopting sustainable consumption practices.
7. What is the importance of the ozone layer?
The ozone layer absorbs most of the sun’s harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation, protecting life on Earth from damaging effects. UV radiation can cause skin cancer, cataracts, and damage to plants and ecosystems.
8. What are aerosols and how do they affect the atmosphere?
Aerosols are tiny particles suspended in the atmosphere, including dust, smoke, sea salt, and volcanic ash. They can influence cloud formation, scatter sunlight, and affect air quality. Some aerosols can reflect sunlight back into space, cooling the planet, while others can absorb heat, warming the planet.
9. How does the atmosphere affect sound transmission?
Sound waves travel through the atmosphere, allowing us to hear. The density and composition of the atmosphere influence the speed and intensity of sound waves.
10. What are some tips for protecting the atmosphere?
- Reduce your energy consumption by using energy-efficient appliances and light bulbs.
- Choose public transportation, cycling, or walking instead of driving.
- Recycle and reuse materials to reduce waste.
- Support sustainable businesses and products.
- Educate yourself and others about environmental issues.
Conclusion
Earth’s atmosphere is a complex and dynamic system that is vital for life on our planet. Understanding its composition, functions, and the impacts of human activities on it is essential for safeguarding its integrity and ensuring a sustainable future for generations to come. By promoting environmental awareness, adopting sustainable practices, and implementing policies that protect the atmosphere, we can preserve this precious resource for future generations.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Earth’s Atmosphere: A Protective Blanket for Life. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!