The Complex Relationship Between Makeup and Acne: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: The Complex Relationship Between Makeup and Acne: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Complex Relationship Between Makeup and Acne: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Complex Relationship Between Makeup and Acne: A Comprehensive Guide
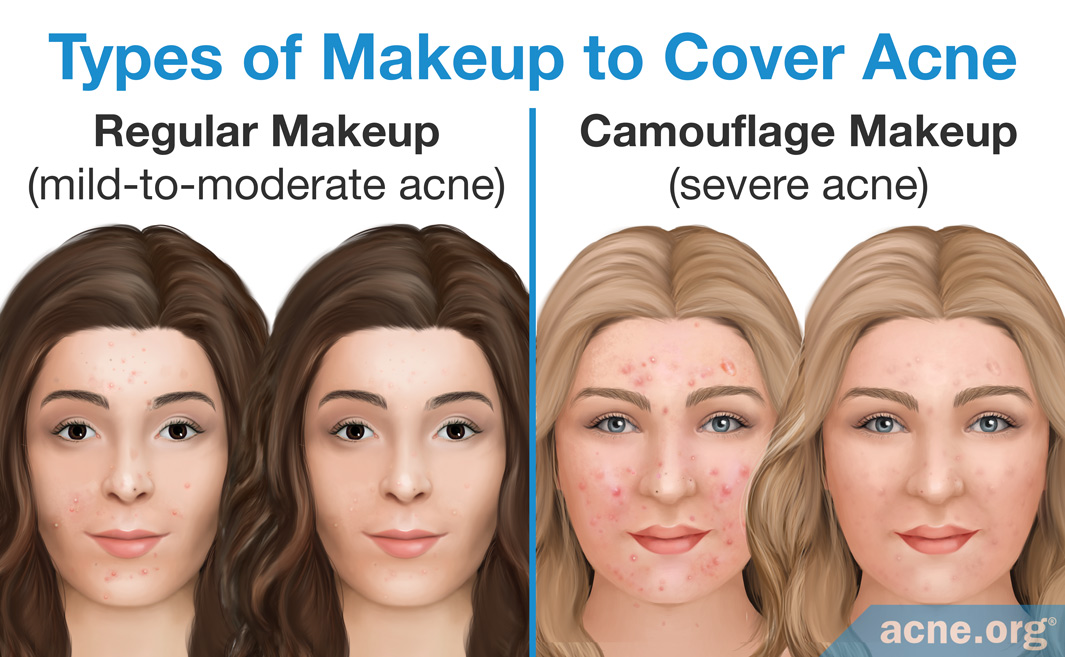

Acne, a common skin condition affecting millions worldwide, often presents a dilemma for individuals seeking to enhance their appearance. The desire to conceal blemishes can lead to the question: does makeup exacerbate acne? While the answer is not always straightforward, a thorough understanding of the factors involved can help individuals make informed choices about their skincare routine.
Understanding the Science of Acne:
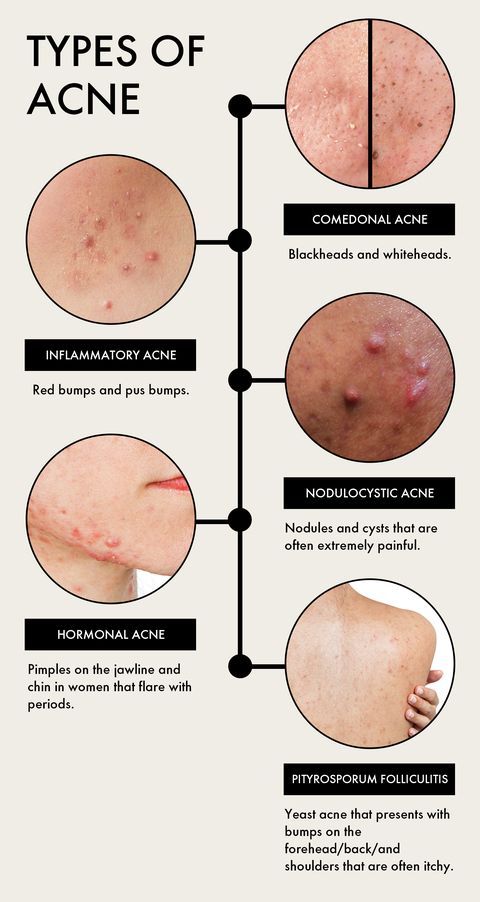
Acne arises from a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Excess Sebum Production: Sebum, an oily substance produced by sebaceous glands, plays a crucial role in lubricating the skin. However, excessive sebum production can clog pores, leading to the formation of comedones (blackheads and whiteheads).
- Hormonal Fluctuations: Hormones, particularly androgens, can stimulate sebaceous gland activity, increasing sebum production and contributing to acne breakouts.
- Bacterial Growth: Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes), a type of bacteria commonly found on the skin, can thrive in clogged pores, leading to inflammation and the characteristic red bumps and pustules associated with acne.
- Inflammation: The body’s immune response to P. acnes and other irritants can trigger inflammation, further aggravating acne lesions.
The Impact of Makeup on Acne:
While makeup itself does not directly cause acne, certain factors related to its application and composition can influence its development:
- Clogged Pores: Makeup, particularly heavy or oily formulas, can contribute to clogged pores. This is especially true if makeup is not removed thoroughly at the end of the day, allowing sebum, dead skin cells, and makeup residue to accumulate in pores.
- Irritating Ingredients: Some makeup ingredients, such as fragrances, dyes, and preservatives, can irritate sensitive skin and trigger inflammation, potentially exacerbating acne.
- Bacterial Contamination: Makeup brushes, sponges, and applicators can harbor bacteria if not cleaned regularly. Applying contaminated makeup can introduce bacteria to the skin, potentially contributing to acne breakouts.
Factors to Consider:
- Skin Type: Individuals with oily or acne-prone skin may be more susceptible to breakouts when using makeup.
- Makeup Formula: Oil-free, non-comedogenic (won’t clog pores), and hypoallergenic makeup formulations are generally considered safer for acne-prone skin.
- Application Technique: Applying makeup with clean hands and tools, and avoiding excessive layering, can minimize the risk of clogged pores and irritation.
- Removal Routine: Thoroughly removing makeup at the end of the day is crucial to prevent pore clogging and bacterial growth.
Tips for Makeup Use with Acne-Prone Skin:
- Choose Non-Comedogenic Products: Look for makeup labeled as "non-comedogenic" or "oil-free," as these are less likely to clog pores.
- Minimize Foundation Coverage: Opt for lightweight foundations or tinted moisturizers, avoiding heavy, thick formulas.
- Use Mineral Makeup: Mineral makeup, typically made with natural ingredients like iron oxides, can be gentler on sensitive skin and less likely to cause irritation.
- Clean Brushes and Tools Regularly: Wash makeup brushes and sponges with a gentle cleanser at least once a week to prevent bacterial buildup.
- Remove Makeup Thoroughly: Use a gentle makeup remover specifically designed for your skin type to remove all traces of makeup before going to bed.
- Consider a Dermatologist Consultation: If you have persistent acne or concerns about the impact of makeup on your skin, consult a dermatologist for personalized advice and treatment options.
FAQs:
Q: Can any type of makeup worsen acne?
A: While not all makeup will worsen acne, certain factors, such as oil content, irritating ingredients, and application techniques, can contribute to breakouts.
Q: Is it better to avoid makeup entirely if I have acne?
A: Avoiding makeup is not always necessary. Choosing the right products and following proper application and removal techniques can minimize the risk of exacerbating acne.
Q: What type of makeup is best for acne-prone skin?
A: Look for oil-free, non-comedogenic, hypoallergenic formulations. Mineral makeup can also be a good option.
Q: How often should I wash my makeup brushes and sponges?
A: It is recommended to wash makeup brushes and sponges at least once a week to prevent bacterial buildup.
Q: Can makeup cause acne scars?
A: Makeup itself does not cause acne scars. However, improper application and removal techniques, as well as using irritating ingredients, can contribute to inflammation and potential scarring.
Conclusion:
The relationship between makeup and acne is complex and multifaceted. While makeup itself does not directly cause acne, certain factors related to its composition, application, and removal can influence its development. By understanding the science of acne and making informed choices about makeup products and application techniques, individuals with acne-prone skin can minimize the risk of breakouts and maintain healthy, radiant skin. Consulting a dermatologist for personalized advice and treatment options can further enhance skincare efforts and address any concerns.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Complex Relationship Between Makeup and Acne: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!