The Complex Relationship Between Makeup and Acne: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: The Complex Relationship Between Makeup and Acne: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Complex Relationship Between Makeup and Acne: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Complex Relationship Between Makeup and Acne: A Comprehensive Guide
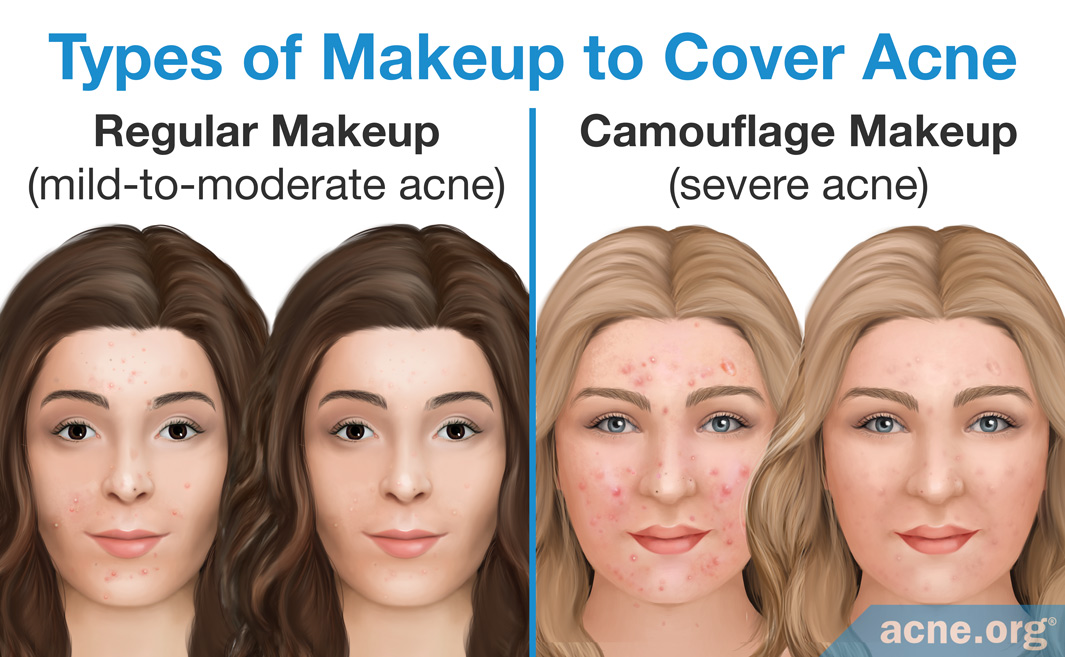

Acne, a common skin condition affecting millions worldwide, is often associated with hormonal fluctuations, genetics, and environmental factors. However, the role of makeup in exacerbating or alleviating acne remains a subject of ongoing discussion and individual experiences. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate relationship between makeup and acne, examining the potential causes, mitigating factors, and best practices for navigating the complexities of skincare and cosmetics.
Understanding Acne: A Primer
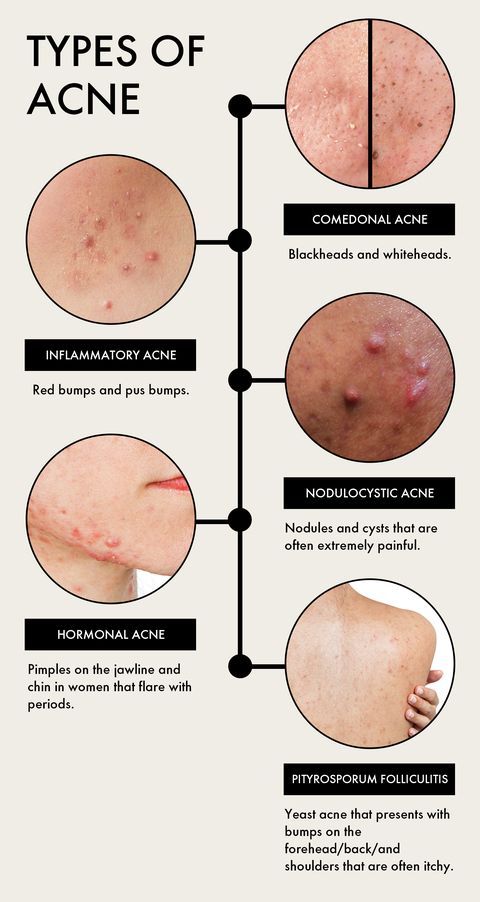
Acne develops when hair follicles become clogged with oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria. This leads to inflammation and the formation of blemishes, ranging from whiteheads and blackheads to painful cysts and nodules. The severity and type of acne can vary significantly based on individual factors.
The Potential Impact of Makeup on Acne:
While makeup itself does not directly cause acne, certain factors related to its use can contribute to breakouts:
- Clogged Pores: Heavy, oil-based makeup, especially foundation and concealers, can trap oil and debris within pores, leading to blockages.
- Comedogenic Ingredients: Some ingredients commonly found in cosmetics, such as mineral oil, lanolin, and certain waxes, are considered comedogenic, meaning they can clog pores and contribute to acne.
- Irritation and Inflammation: Harsh ingredients, fragrances, or preservatives in makeup can irritate sensitive skin, leading to inflammation and increased acne.
- Improper Application and Removal: Applying makeup with unclean hands or tools, or failing to remove it completely before bed, can introduce bacteria and debris into pores, exacerbating acne.
Factors Influencing the Impact of Makeup on Acne:
The relationship between makeup and acne is not straightforward and is influenced by several factors:
- Skin Type: Individuals with oily or acne-prone skin are more susceptible to breakouts when using certain makeup products.
- Product Formulation: Oil-free, non-comedogenic, and hypoallergenic makeup options are generally considered less likely to contribute to acne.
- Application Technique: Proper application, using clean tools, and avoiding excessive layering can minimize the risk of clogged pores.
- Individual Sensitivity: Some individuals may be more sensitive to specific ingredients or formulations, experiencing breakouts even with products considered non-comedogenic.
Navigating Makeup and Acne: Practical Tips
While makeup can potentially contribute to acne, it does not have to be a barrier to achieving a desired look. Following these tips can help minimize the risk of breakouts:
- Choose Non-Comedogenic Products: Opt for makeup labeled "non-comedogenic," "oil-free," and "hypoallergenic" to reduce the likelihood of clogged pores.
- Check Ingredient Lists: Avoid ingredients known to be comedogenic, such as mineral oil, lanolin, and certain waxes.
- Prioritize Lightweight Formulas: Opt for lighter, water-based foundations and concealers that allow skin to breathe.
- Cleanse Thoroughly: Remove all makeup before bed using a gentle, non-irritating cleanser.
- Exfoliate Regularly: Regular exfoliation helps remove dead skin cells and prevent pore blockage.
- Use Clean Brushes and Sponges: Wash makeup brushes and sponges regularly to prevent bacteria buildup.
- Avoid Touching Your Face: Touching your face throughout the day can transfer bacteria and oil to your skin.
- Seek Professional Guidance: Consult a dermatologist for personalized advice on skincare and makeup choices.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns
Q: Does wearing makeup every day make acne worse?
A: Not necessarily. The impact of makeup on acne depends on the type of makeup, individual skin sensitivity, and application practices. Choosing non-comedogenic products and practicing good hygiene can minimize the risk of breakouts.
Q: Is it okay to wear makeup if I have acne?
A: Yes, but it is essential to choose products carefully and prioritize good hygiene. Opt for non-comedogenic and oil-free makeup, and ensure thorough cleansing and removal.
Q: What types of makeup are best for acne-prone skin?
A: Look for products labeled "non-comedogenic," "oil-free," and "hypoallergenic." Water-based foundations and concealers are generally preferred over oil-based formulas.
Q: Can makeup worsen existing acne?
A: Yes, certain makeup products and application practices can exacerbate existing acne. Clogged pores, irritation, and bacterial contamination can worsen breakouts.
Q: Should I stop wearing makeup entirely if I have acne?
A: Not necessarily. Choose products wisely, practice good hygiene, and consider consulting a dermatologist for personalized advice.
Conclusion
The relationship between makeup and acne is complex and multifaceted. While makeup can contribute to breakouts in some individuals, it does not have to be a barrier to achieving a desired look. By choosing non-comedogenic products, practicing good hygiene, and understanding individual skin sensitivity, individuals can minimize the risk of acne and enjoy the benefits of makeup without compromising their skin health. Remember, consulting a dermatologist for personalized advice is always recommended for managing acne and navigating the complexities of skincare and cosmetics.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Complex Relationship Between Makeup and Acne: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!