Unveiling the Secrets of Reflection: A Comprehensive Guide to Concave and Convex Mirrors
Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of Reflection: A Comprehensive Guide to Concave and Convex Mirrors
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Secrets of Reflection: A Comprehensive Guide to Concave and Convex Mirrors. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Secrets of Reflection: A Comprehensive Guide to Concave and Convex Mirrors

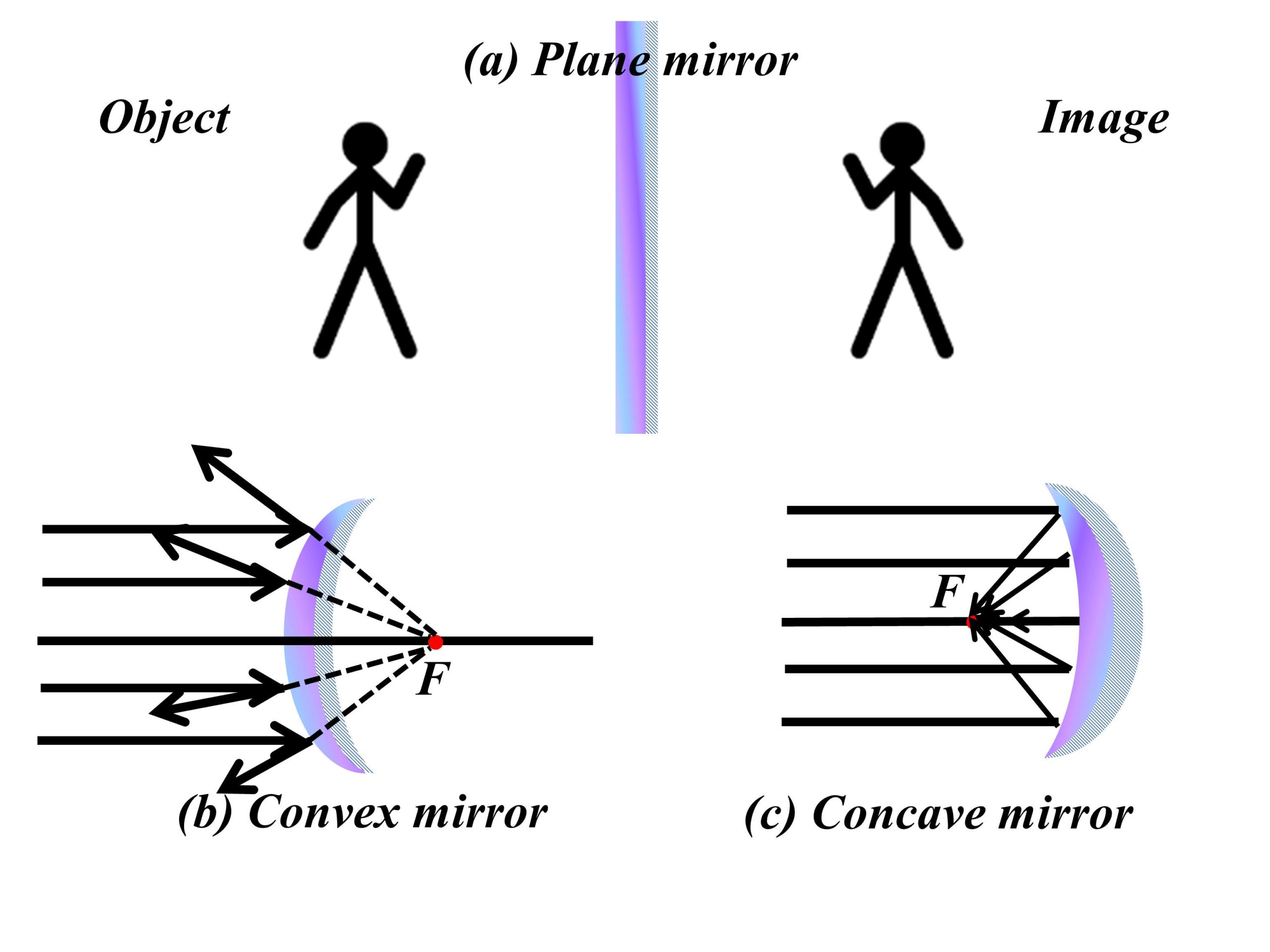
Mirrors, ubiquitous in our daily lives, play a crucial role in shaping our perception of the world. Their ability to reflect light, however, is not uniform. Two primary types of mirrors, concave and convex, exhibit distinct reflective properties, leading to unique applications and fascinating optical phenomena. Understanding the fundamental differences between these mirrors is essential for appreciating their diverse uses and the science behind their function.
Defining the Differences: Concave vs. Convex
The defining characteristic that distinguishes concave and convex mirrors lies in the curvature of their reflecting surface. A concave mirror possesses an inward curve, resembling the inside of a spoon. Conversely, a convex mirror has an outward curve, similar to the outside of a spoon. This seemingly simple difference leads to contrasting behaviors in how they reflect light.
The Power of Concave Mirrors: Converging Light and Magnification
Concave mirrors are known for their ability to converge light rays. When parallel rays of light strike a concave mirror, they are reflected inwards, converging at a single point called the focal point. This converging property gives rise to several unique applications:
- Magnification: Concave mirrors can magnify objects, making them appear larger. This principle is utilized in magnifying glasses, telescopes, and even dental mirrors, allowing for detailed examination of small objects.
- Focusing Light: The ability to converge light makes concave mirrors ideal for concentrating light energy. This principle is employed in solar cookers, where sunlight is focused onto a single point, generating heat for cooking.
- Reflecting Light: Concave mirrors can also be used to reflect light in a specific direction. This property is utilized in car headlights and flashlights, where the light is focused into a narrow beam.
The Wide-Angle Vision of Convex Mirrors: Diverging Light and Wider Fields
Convex mirrors, on the other hand, are characterized by their ability to diverge light rays. When parallel rays of light strike a convex mirror, they are reflected outwards, appearing to emanate from a single point behind the mirror, known as the virtual focal point. This diverging property leads to a unique set of applications:
- Wide Field of View: Convex mirrors provide a wider field of view compared to plane mirrors. This property is exploited in security mirrors, used in stores and parking garages to provide a wider surveillance area.
- Rearview Mirrors: Convex mirrors are commonly used as rearview mirrors in vehicles, offering a wider view of the road behind the car, enhancing safety.
- Telescopes: Convex mirrors are also used in some types of telescopes, particularly reflecting telescopes, where they serve as primary mirrors to gather and focus light from distant objects.
Understanding the Image Formation: Real vs. Virtual Images
The distinct reflective properties of concave and convex mirrors result in different types of image formation.
- Concave Mirrors: Concave mirrors can form both real and virtual images. Real images are formed when light rays converge and intersect at a point, creating an image that can be projected onto a screen. Virtual images, on the other hand, are formed when light rays appear to converge behind the mirror, creating an image that cannot be projected onto a screen. The nature of the image formed by a concave mirror depends on the position of the object relative to the mirror.
- Convex Mirrors: Convex mirrors always form virtual images. This is because the light rays diverge after reflection, never converging to form a real image. Virtual images formed by convex mirrors are always upright and smaller than the object.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Applications and Applications
The unique properties of concave and convex mirrors extend their applications beyond simple reflection.
Concave Mirrors in Technology:
- Satellite Dishes: Concave satellite dishes are designed to focus radio waves from satellites, enabling reception of television signals.
- Reflecting Telescopes: Concave mirrors are used as primary mirrors in reflecting telescopes, gathering and focusing light from distant stars and galaxies.
- Dental Mirrors: Concave mirrors are used in dentistry to magnify teeth and provide a clearer view for examination and treatment.
Convex Mirrors in Everyday Life:
- Security Mirrors: Convex mirrors are used in stores and parking garages to provide a wider field of view, enhancing security and safety.
- Rearview Mirrors: Convex mirrors are commonly used as rearview mirrors in vehicles, offering a wider view of the road behind the car, enhancing safety.
- Side Mirrors: Convex mirrors are also used as side mirrors in vehicles, providing a wider view of the lane next to the car, reducing blind spots.
Beyond Reflection: Exploring the Physics of Mirrors
The behavior of light reflected by concave and convex mirrors can be explained by the laws of reflection. These laws state that:
- Angle of Incidence equals Angle of Reflection: The angle at which light strikes a mirror (angle of incidence) is equal to the angle at which it is reflected (angle of reflection).
- Incident Ray, Reflected Ray, and Normal lie in the same Plane: The incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal (a line perpendicular to the mirror surface at the point of incidence) all lie in the same plane.
FAQs: Demystifying the Mysteries of Concave and Convex Mirrors
Q: What is the difference between a concave and a convex mirror?
A: A concave mirror has an inward curve, while a convex mirror has an outward curve. This difference in curvature leads to distinct reflective properties, with concave mirrors converging light and convex mirrors diverging light.
Q: What are some common applications of concave mirrors?
A: Concave mirrors are used in magnifying glasses, telescopes, satellite dishes, solar cookers, car headlights, and dental mirrors.
Q: What are some common applications of convex mirrors?
A: Convex mirrors are used in security mirrors, rearview mirrors, side mirrors, and some types of telescopes.
Q: Can concave mirrors form real images?
A: Yes, concave mirrors can form both real and virtual images, depending on the position of the object relative to the mirror.
Q: Can convex mirrors form real images?
A: No, convex mirrors can only form virtual images.
Q: What are the laws of reflection?
A: The laws of reflection state that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection, and that the incident ray, reflected ray, and normal lie in the same plane.
Tips for Understanding Concave and Convex Mirrors
- Visualize the Curvature: Imagine the shape of a spoon to understand the difference between concave and convex mirrors.
- Experiment with Light: Shine a flashlight onto a concave mirror and observe how the light converges. Do the same with a convex mirror and observe how the light diverges.
- Draw Ray Diagrams: Use ray diagrams to visualize how light rays are reflected by concave and convex mirrors.
- Explore Real-World Examples: Observe the use of concave and convex mirrors in everyday objects like magnifying glasses, telescopes, and rearview mirrors.
Conclusion: Embracing the Wonders of Reflection
Concave and convex mirrors, despite their seemingly simple design, offer a fascinating glimpse into the world of reflection. Their unique properties, ranging from magnification to wide-angle vision, have revolutionized our understanding of light and its interaction with surfaces. By understanding the fundamental differences between these mirrors, we can appreciate their diverse applications and the scientific principles that govern their behavior. From magnifying small objects to enhancing our vision on the road, concave and convex mirrors continue to shape our world, reminding us of the wonders of light and reflection.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Secrets of Reflection: A Comprehensive Guide to Concave and Convex Mirrors. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!